carbonyl compounds examples 06.02 nomenclature of carbonyl compounds
The carbonyl group is an important functional group in organic chemistry. It consists of a carbon atom double-bonded to an oxygen atom, known as the carbonyl carbon. This group can be found in a wide range of compounds, including aldehydes, ketones, carboxylic acids, esters, and amides. In this post, we will explore the nomenclature and structure of the carbonyl group, provide examples, and delve into some related concepts. So, let’s dive right in!
Nomenclature and Structure
To name compounds containing a carbonyl group, we usually follow a set of rules. For aldehydes, the suffix “-al” is added to the name of the parent chain. Ketones, on the other hand, get the suffix “-one.” The carbon atom of the carbonyl group is always considered the first carbon of the parent chain. In terms of structure, the carbon-oxygen double bond gives the carbonyl group a unique arrangement. The carbon atom is trigonal planar, while the oxygen atom has a lone pair of electrons, resulting in a bent shape. 
Examples of Carbonyl Compounds
Carbonyl compounds are incredibly diverse and play vital roles in various biological and chemical processes. Let’s take a look at a few examples:
1. Aldehydes
Aldehydes have a carbonyl group at the end of the carbon chain. One well-known example is formaldehyde, which is used in embalming and as a disinfectant. Another common aldehyde is acetaldehyde, which is responsible for the hangover symptoms after consuming alcoholic beverages.
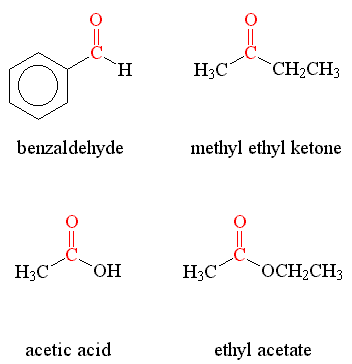 ### 2. Ketones
### 2. Ketones
Ketones have a carbonyl group in the middle of the carbon chain. Acetone, also known as propanone, is the simplest and most well-known ketone. It is widely used as a solvent and is also an important intermediate in many chemical syntheses.
 ### 3. Carboxylic Acids
### 3. Carboxylic Acids
Carboxylic acids have a carbonyl and a hydroxyl group (OH) on the same carbon atom. An example is acetic acid, which is found in vinegar and has a sour taste. Carboxylic acids are essential building blocks in biological systems and are involved in processes like metabolism and signaling.
4. Amides
Amides are formed when a carbonyl group reacts with an amine compound. One well-known example is acetamide, which is used in the production of pharmaceuticals and dyes. Amides also play a crucial role in protein structure and function.
These are just a few examples of the diverse range of compounds that contain a carbonyl group. It is fascinating to see how this functional group can affect the properties and reactivity of different molecules.
In conclusion, the carbonyl group is a significant functional group in organic chemistry. Its unique structure and diverse range of compounds make it an important area of study. Whether you are interested in synthesizing new molecules, understanding biological processes, or simply curious about the world of chemistry, exploring the carbonyl group and its compounds is a great place to start!
If you are looking for 06.02 Nomenclature of Carbonyl Compounds - YouTube you’ve visit to the right web. We have 5 Images about 06.02 Nomenclature of Carbonyl Compounds - YouTube like Carbonyl Group: Nomenclature and Structure, Examples, Videos, Q&A, 06.02 Nomenclature of Carbonyl Compounds - YouTube and also 06.02 Nomenclature of Carbonyl Compounds - YouTube. Read more:
06.02 Nomenclature Of Carbonyl Compounds - YouTube
 www.youtube.comcarbonyl compounds nomenclature
www.youtube.comcarbonyl compounds nomenclature
Introduction - Carbonyl Compounds
chemistry.elmhurst.educhemistry carbonyl compounds ketones aldehydes group perfume ketone aldehyde structure carbon double introduction organic functional bond gif chemical manash subhaditya
Structure Of Carbonyl Group - Tranny Body Perfect
 www.feesdyvert.comcarbonyl compounds polarity bonding benzene electronegativity chem
www.feesdyvert.comcarbonyl compounds polarity bonding benzene electronegativity chem
Carbonyl Group: Nomenclature And Structure, Examples, Videos, Q&A
 www.toppr.comcarbonyl group structure nomenclature examples members chemistry wikipedia source
www.toppr.comcarbonyl group structure nomenclature examples members chemistry wikipedia source
Re: What Is A Carbonyl Group?
 www.madsci.orgcarbonyl compounds group examples groups shown notice above
www.madsci.orgcarbonyl compounds group examples groups shown notice above
Re: what is a carbonyl group?. Carbonyl compounds polarity bonding benzene electronegativity chem. Structure of carbonyl group